Diabetic foot
Diabetic foot refers to a condition that affects individuals with diabetes, leading to complications and potential damage to the feet. It is a serious condition that requires proper management and care to prevent further complications, including infections and even amputation. Here’s some information about diabetic foot and its management:
Foot Complications in Diabetes: Diabetes can cause a range of foot complications due to poor circulation, nerve damage (neuropathy), and impaired wound healing. These complications include diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage), peripheral arterial disease (poor blood flow), foot ulcers, infections, Charcot foot (deformity), and gangrene. It is crucial for individuals with diabetes to be vigilant about foot care to prevent these complications.
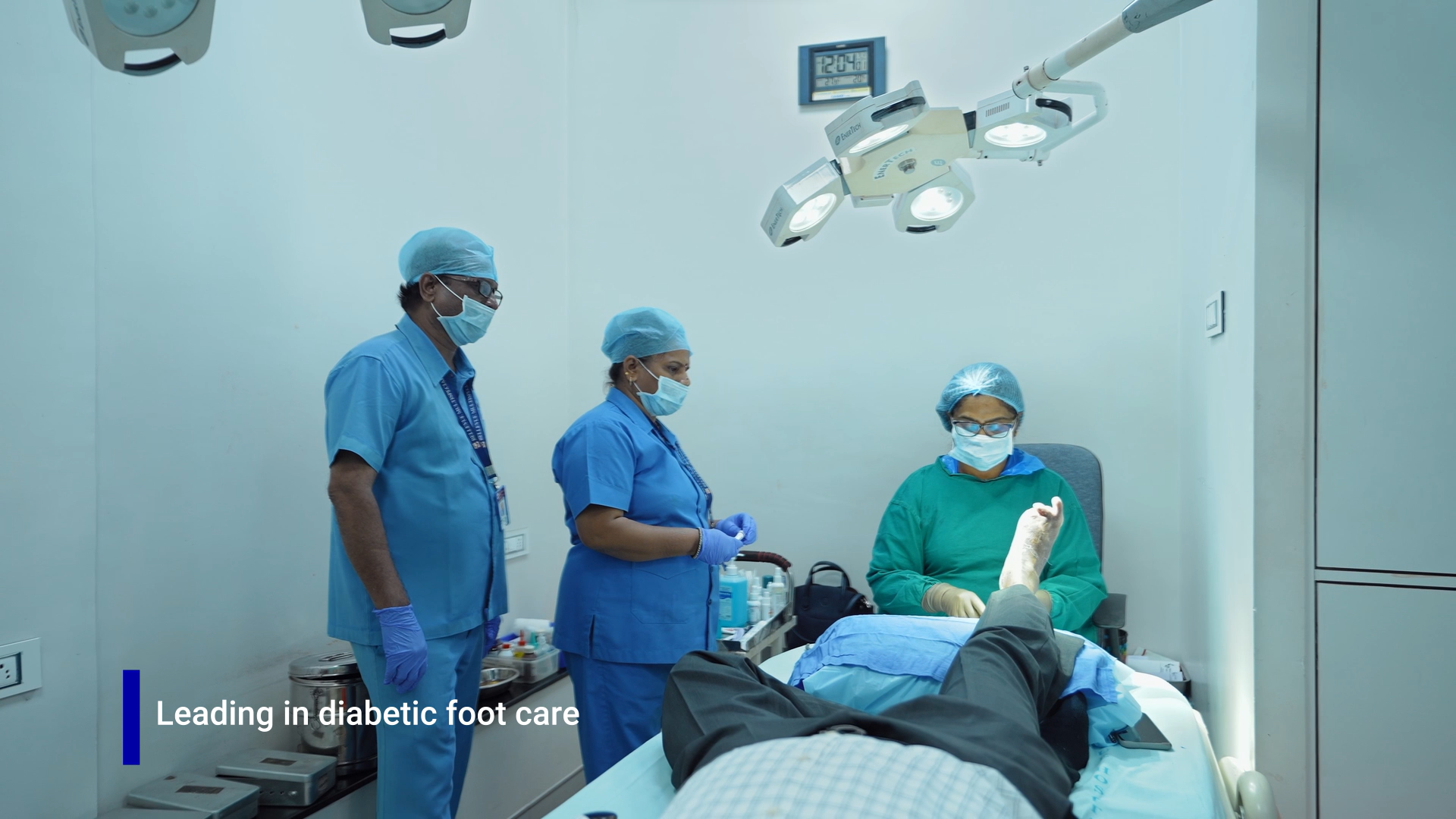
Importance of Foot Care: Regular foot care is essential for individuals with diabetes to maintain foot health and prevent diabetic foot complications. This includes daily foot inspections for any signs of redness, swelling, blisters, cuts, or other abnormalities. Proper foot hygiene, regular nail trimming, and wearing well-fitting shoes and socks are also important. It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for guidance on foot care techniques and self-examinations.
Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that develop on the feet. They typically occur due to a combination of factors, including neuropathy, poor circulation, and pressure from ill-fitting footwear. Diabetic foot ulcers require specialized treatment and management to promote healing and prevent infection. This may include wound dressings, offloading devices, regular debridement (removal of dead tissue), and antibiotic therapy if necessary.
Multidisciplinary Foot Care Team: The management of diabetic foot often involves a multidisciplinary approach. A team of healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists, podiatrists, wound care specialists, vascular surgeons, and infectious disease specialists, collaborate to provide comprehensive care. This team approach ensures a holistic evaluation and treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
Offloading and Pressure Redistribution: Offloading techniques aim to reduce pressure on the foot ulcers and promote healing. This may involve the use of specialized footwear, casts, braces, or orthotic devices to redistribute pressure and protect the affected areas. Offloading helps to relieve pressure on the ulcers, allowing the wounds to heal more effectively.
Education and Self-Management: Education plays a crucial role in the prevention and management of diabetic foot complications. Individuals with diabetes should receive proper education on foot care techniques, including daily self-inspection, appropriate footwear selection, and prompt reporting of any abnormalities to their healthcare provider. Self-management skills empower individuals to take an active role in preventing complications and seeking timely medical intervention.
It is important for individuals with diabetes to prioritize foot care and undergo regular foot examinations by healthcare professionals specializing in diabetic foot management. By adopting a proactive approach to foot health and adhering to the recommended preventive measures and treatment plans, the risk of diabetic foot complications can be significantly reduced.
